Interview Questions & Answers
📘 INTRODUCTION TO DATA ANALYTICS
Q1. What is Data Analytics? +
Data Analytics is the process of collecting, cleaning, and analyzing data to discover useful information. It helps businesses make better decisions by identifying patterns and trends. Data Analytics focuses on understanding past and present data. It supports decision-making across industries.
Q2. Why is Data Analytics important for businesses? +
Data Analytics helps businesses understand customer behavior and improve performance. It allows companies to reduce risks and increase efficiency. Analytics supports strategic planning using data rather than assumptions. It improves accuracy in business decisions.
Q3. What are the main types of Data Analytics? +
The main types are Descriptive, Diagnostic, Predictive, and Prescriptive Analytics. Descriptive explains what happened, diagnostic explains why it happened. Predictive forecasts future outcomes, and prescriptive suggests actions. Each type serves a different business purpose.
Q4. What is the role of a Data Analyst? +
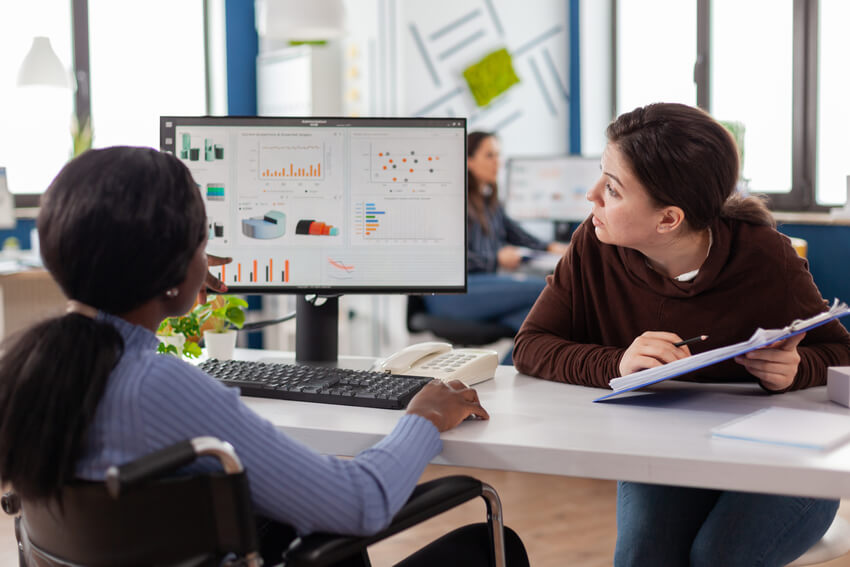
A Data Analyst collects and analyzes data to generate insights. They create reports, dashboards, and summaries for decision-makers. The role involves data cleaning and visualization. Communication skills are important to explain insights clearly.
Q5. Is Data Analytics suitable for freshers? +
Yes, Data Analytics is suitable for freshers because it starts with basic concepts. It does not require advanced programming knowledge. Logical thinking and practice are more important. With proper training, freshers can build strong careers.
Q6. What tools are commonly used in Data Analytics? +
Common tools include Excel, SQL, Python, and Power BI. Excel is used for basic analysis and reporting. SQL is used to work with databases. Power BI and Python help in visualization and advanced analysis.
Q7. How is Data Analytics different from Data Science? +
Data Analytics focuses on analyzing existing data for insights. Data Science includes advanced concepts like machine learning and AI. Analytics is more business-oriented and beginner-friendly. Data Science requires deeper technical skills.
📘 UNDERSTANDING DATA & ITS IMPORTANCE
Q1. What is data? +
Data is a collection of facts, numbers, or information. It can be in the form of text, numbers, images, or videos. Data is collected from various sources. It is the foundation for analysis and decision-making.
Q2. Why is data important in organizations? +
Data helps organizations understand performance and customer behavior. It supports planning and problem-solving. Businesses use data to improve efficiency. Data-driven decisions reduce risks.
Q3. What are real-world examples of data usage? +
E-commerce companies analyze customer purchases. Banks analyze transaction data for fraud detection. Hospitals analyze patient data for better treatment. Data is used in almost every industry today.
Q4. What is raw data? +
Raw data is unprocessed and unorganized information. It may contain errors or missing values. Raw data is not directly useful for decision-making. It must be cleaned and processed.
Q5. How does data help in decision-making? +
Data provides factual insights instead of assumptions. It helps compare options and outcomes. Decisions become more accurate with data support. Analytics reduces uncertainty in business decisions.
Q6. What is structured data? +
Structured data is organized in rows and columns. It is easy to store in databases. Examples include Excel sheets and SQL tables. It is easy to analyze.
Q7. What is unstructured data? +
Unstructured data has no fixed format. Examples include emails, videos, and social media posts. It is harder to analyze. Special tools are required to process it.
📘 DATA BASICS & DATA HANDLING
Q1. What are the main types of data? +
The main types are structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Structured data is organized, semi-structured has some format, and unstructured has no format. Each type requires different handling methods.
Q2. What are data sources? +
Data sources are places from where data is collected. Examples include databases, surveys, websites, and sensors. Data can be internal or external. Reliable sources are important for accuracy.
Q3. What is data lifecycle? +
Data lifecycle refers to stages like collection, storage, processing, analysis, and reporting. Each stage plays an important role. Proper handling ensures data quality. It helps manage data efficiently.
Q4. What are data formats? +
Data formats define how data is stored. Examples include CSV, Excel, JSON, and XML. Different tools support different formats. Choosing the right format is important for analysis.
Q5. What is data collection? +
Data collection is the process of gathering information. It can be done through surveys, systems, or sensors. Accurate data collection is essential. Poor data leads to poor analysis.
Q6. What is data storage? +
Data storage means saving data securely. It can be stored in databases or cloud systems. Proper storage ensures data availability. Security is an important aspect.
Q7. What is data processing? +
Data processing involves cleaning and transforming data. Errors and duplicates are removed. Data becomes ready for analysis. This step improves data quality.